JavaScript Part 2 Class 12 Web Application Code 803 NCERT Book Solution
I. Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which of the following statements is not true for JavaScript:
a. JavaScript is a compiled language.
b. In JavaScript an interpreter in the browser reads over the JavaScript code.
c. Any error found in the code, will stop the further execution of the program.
d. JavaScript can be implemented using tags.
2. A script cannot be placed
a. In the body of the page
b. In the header of the page
c. In a file with extension .js
d. In a file with extension .css
3. Which of the following is an advantage of JavaScript?
a. It can be used for client-side and server-side i.e. front end and back end.
b. It runs on multiple platforms and devices.
c. It is supported by all browsers.
d. All of the above.
4. Which of these is not a Primitive Data Type in JavaScript?
a. Boolean
b. Undefined
c. Arrays
d. Strings
5. In JavaScript adding a number and a string will return ______.
a. a string
b. a number
c. NaN
d. None of these
6. Which of the following cannot be a variable?
a. _new
b. y24
c. Val
d. 5g
7. Which of the following statements is not true for Variables in JavaScript?
a. Variables in JavaScript can be defined using the keyword var.
b. The equal to (=) sign is used to assign a value to a variable.
c. We cannot assign null to a variable.
d. A variable can be undefined.
8. Which of the following is an Arithmetic operator?
a. +=
b. ==
c. – –
d. *=
9. When we use a comparison operator the datatype of the output is always:
a. Integer
b. Boolean
c. NaN
d. Undefined
10. What will be the value returned by the following expression?
34 && -10
a. true
b. false
c. 34
d. -10
11. What will be the value returned by the following expression?
0 || -20
a. true
b. false
c. -20
d. 0
12. Which of the following statements is not true for function arguments/parameters?
a. Function parameters are listed between parenthesis ( ).
b. The number of function parameters is fixed.
c. Function arguments are the values that the function receives when it is called.
d. The arguments (parameters) act as local variables within the function.
13. In JavaScript, the definition of a function starts _______.
a. with the return type, function keyword, function name and parentheses.
b. with the function keyword, function name and parentheses.
c. with the return type, function name and parenthesis.
d. with the function name, parenthesis and return type.
14. For the provided JavaScript code, which of the following is the correct output?
var values=[4,5,6,7]
var ans=values.slice(1);
document.write(ans);
a. Error
b. 5, 6, 7
c. 4, 5, 6,
d. 4, 5, 6, 7
15. What will typeof(null) return/output?
a. object
b. null
c. undefined
d. nothing
16. For the JavaScript code provided, which of the following is the correct output?
var values = [“Three”, “Two”, “One”];
var ans=values.shift();
document.write(ans);
a. One
b. Three
c. Two
d. error
17. Of the following, which method of the Array object is used to extend an array by one or more members and return the array’s new length?
a. splice()
b. unshift()
c. sort()
d. toString()
18. Out of all the built-in methods, which one is used for removing the last element from an array and return it?
a. pop()
b. last()
c. get()
d. shift()
19. Which event occurs when a webpage has finished loading the page?
a. onload
b. onready
c. onloaded
d. unload
20. The syntax for replaceAll( ) is______.
a. string.replaceAll(searchValue, newValue)
b. string.replace(searchValue, newValue)
c. string.replaceall(searchValue, newValue)
d. None of the above
21. What will the following JavaScript code snippet output?
var x = “Hello, Include Hello”;
document.write(x.slice(-13, -1))
a. IncludeHelp!
b. IncludeHelp
c. ValueError
d. Hello,
22. What will the following JavaScript code snippet output?
var myArray = [‘h’, ‘e’, ‘l’, ‘l’, ‘o’];
document.write(myArray[0]);
document.write(myArray[1]);
a. undefined
b. he
c. ValueError
d. TypeError
23. What will the following JavaScript code output?
document.write(Math.round(117.5));
a. 117.5
b. 117
c. 118
d. 117.00
24. Which of the following cannot be an output for
document.write(Math.random()*10)
a. 8.49259898
b. 1.78925374
c. 0
d. 10
25. What happens when a user changes the content of a textbox in the following?
<input type=”text” onchange=”myFunction()”>
a. The user enters the content in the text box.
b. The user gets a message to change the content.
c. The function myFunction( ) gets invoked.
d. The user cannot change the content.
JavaScript Part 2 Class 12 Web Application Code 803 NCERT Book Solution
II. List the Built-in function for each of the Following:
1. A function to take user input as string.
Ans: prompt()
2. The function used to convert to an integer.
Ans:
3. A function to convert to a floating-point number.
Ans: parseFloat( )
4. A function to check if something is Not a Number.
Ans: isNaN()
5. Used to display data or a message in a box on the window.
Ans: alert( )
III. Write the events for the following:
1. As soon as the user presses and releases the key.
Ans: Event: keydown
Event Handler: onkeydown
2. After the browser has finished loading the page.
Ans: Event: load
Event Handler: onload
3. When an individual edits the form element’s value.
Ans: Event: change
Event Handler: onchange
4. When the mouse pointer leaves an element.
Ans: Event: mouseout
Event Handler: onmouseout
5. When the mouse pointer comes over the element.
Ans: Event: mouseover
Event Handler: onmouseover
JavaScript Part 2 Class 12 Web Application Code 803 NCERT Book Solution
IV. What will be the output of the following codes.
Que 1. Find output:
<!-- Question 1 -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript Functions</h2>
<p id="demo1"></p>
<p id="demo2"></p>
<script>
var x=170;
function myFunction()
{
var x=45;
document.getElementById('demo1').innerHTML= x;
}
document.getElementById("demo2").innerHTML= x+20;
myFunction();
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:

Que 2. Find output:
<!-- Question 2 -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html
<body>
<script>
lang1=['java','rust','ruby']
lang2=['haskell','python']
lang1=lang1.concat(lang2)
lang1.sort()
lang1.reverse()
document.write(lang1)
</script>
</bodv>
</html>
Output: rust,ruby,python,java,haskell
Que 3. Find output:
<!-- Question 3 -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript Functions</h2>
<p id="demo1"></p>
<p id="demo2"></p>
<script>
var x = 55;
var y = 15;
function myFunction()
{
var x = 100;
var y = 40;
x++;
return x+y ;
}
document.getElementById("demo2").innerHTML= x+y;
document.getElementById("demo1").innerHTML = myFunction();
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:

Que 4. Find output:
<!-- Question 4 -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html
<body>
<p id="Far"></p>
<p id="Cel"></p>
<script>
function toCelsius(temp) {
return (5/9) * (temp-32);
}
function toFarhenheit(temp){
return (9/5) * temp+32;
}
document.getElementById("Far").innerHTML = toFarhenheit(18);
document.getElementById("Cel").innerHTML = toCelsius(32);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:

Que -5. Find output:
<!-- Question 5 -->
<html>
<body>
<script>
x = Math.max(66.7,81.9,-100.5);
y = Math.min(66.7,81.9,-100.5);
z = Math.ceil(x+y);
document.write("x = "+x + "<br>");
document.write("y = "+y + "<br>");
document.write("z = "+z + "<br>");
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:

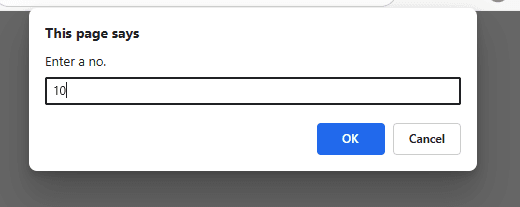
Que 6. Find output:
<!-- Question 6 -->
<html>
<body>
<script>
var y = 0;
var p = parseInt(prompt("Enter a no."));
function checkprime(n) {
for(var x = 2;x < n; x++) {
if (n % x == 0)
{
document.write ("The number is not prime"+"<br>");
y = 1
break;
}
}
if(y == 0) {
document.write ("The number is prime"+"<br>");
}
}
checkprime(16);
checkprime(23);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:

JavaScript Part 2 Class 12 Web Application Code 803 NCERT Book Solution
V. What is the syntax or logical Error in the following codes? Rewrite the code with the correct syntax and underline the errors.
Que 1. A function to find whether the number is odd or even.

Ans:
function chknum(a)
{
if( a % 2 == 0) {
document.write(“The number is even”+”<br>”); }
else { document.write(“The number is odd”+”<br>”) } }
Errors: (a) function must be in small letter.
(b) Variable n is not declared.
(c) In place of variable n, variable a should be used.
(d) In place of not equal to (!=), equal to (==) will be used.
Que 2. A function to find the sum of 3 numbers.

Ans:
function sumfunc(a, b, c)
{
return a+b+c;
}
var sum = sumfunc(6,4,3) ;
document.getElementById(“demo1”).innerHTML = sum ;
Errors:
(a) Variable ‘A’ not should be ‘a’
(b) var keword must be in small letter.
(c) name of function is ‘sumfunc’ instead of SumFunc.
(d) variable name is sum, not Sum.
(e) write semicolon after end of each statement.
Que 3. A function to find the value of a number raised to power another number using the Math object method.

Ans:
<script>
function powerFunction(p1, p2) {
retrun Math.pow(p1, p2);
}
document.write(powerFunctioin(4,3) ) ;
</script>
Errors:
(a) Name of power function is pow( ).
(b) In userdefined function F is a capital letter.
Que 4. A function to merge strings

Ans:
<script>
function myFunction ( ) {
var str1 = “Welcome”;
var str2 = “to JavaScript”;
var str3 = “String Object!”;
var res = str1.Concatenate(str2, str3);
document.getElementById(“demo”).innerHTML = result;
}
</script>
Error:
(a) Use small bracket i.e. parenthesis, after the function name.
(b) The string function name is concat(),
Que 5. Program to find a character in a string

Ans:
<script>
var str = “Welcome to JavaScript”;
document.getElementById(“demo3”).innerHTML = str.charAt(11);
</script>
Error: Function name is charAt( ) to get the character at given index position.
Que 6. A function to change the case in a string.

Ans: Corrected Code:
<script>
function UpperStr( ) {
var str = “Changing String Objects”;
var res = str.toUpperCase( );
document.getElementById(“demo”).innerHTML = res;
</script>
Errror: The function name is toUpperCase () to convert in upper case.
VI. Write the code for the following
1. Write a program with 2 functions to find simple or compound interest depending on user input, also take user input for principal, rate and time.
Ans:
// Function to calculate Simple Interest
function simpleInterest(p, r, t) {
return (p * r * t) / 100;
}
// Function to calculate Compound Interest
function compoundInterest(p, r, t) {
return p * (Math.pow((1 + r / 100), t)) - p;
}
// Taking user input
let principal = parseFloat(prompt("Enter Principal Amount: "));
let rate = parseFloat(prompt("Enter Rate of Interest: "));
let time = parseFloat(prompt("Enter Time (in years): "));
let type = prompt("Enter 'SI' for Simple Interest or 'CI' for Compound Interest: ").toUpperCase();
// Decision based on user input
if (type === "SI") {
let si = simpleInterest(principal, rate, time);
alert("Simple Interest = " + si.toFixed(2));
}
else if (type === "CI") {
let ci = compoundInterest(principal, rate, time);
alert("Compound Interest = " + ci.toFixed(2));
}
else {
alert("Invalid input! Please enter SI or CI.");
}
2. Write a program where a function MyFunc( ) it takes the user name and displays a message”
Hello username welcome to this page!
function MyFunc() {
// Take user input
var username = prompt("Enter your name:");
// Display message
alert("Hello " + username + " welcome to this page!");
}
// Call the function
MyFunc();
3. Write a program with a function to find the smallest out of 3 numbers.
4. Write a program with a function to take user input in kilograms and convert it to grams. [1 Kilogram=1000 grams]
a
5. Write a program with a function sortnum( ) to sort 3 numbers in ascending order.
a
6. Using a button call a function Pytha( ) and take the input for the sides then check whether a number is a Pythagorean Triplet or not.
a
7. Write a program with a function called through a button to ask user age and if the age is greater than 18, display the message “You are eligible” in a paragraph.
a
VII. Answer the Following Questions:
1. Give an example to explain the JavaScript functions and arrays.
2. Describe the JavaScript terms object methods and object properties.
3. Using two examples, describe the JavaScript event handler.
4. Create a JavaScript function that will delete the last element and show the name in uppercase from an array arr1 that was passed to it as an argument.
5. Differentiate between JavaScript’s ceil and floor methods of the Math Object.
6. Declare a function ‘stringsjava’ in JavaScript to accept two strings arguments. The function should
a. Convert both the strings to lowercase
b. Search for string1 in string2 and display the string if found.
c. Replace all occurrences of letter ‘I’ with ‘ ! ‘ in string2.
d. Display the first character of string1.
7. Consider the following code:
var cars = [“Honda”, “BMW”, “Audi”, “Porsche”];
Write command in JavaScript to :
a. add an item “Volvo “ to the array cars in the last.
b. remove first element from the array.
c. display number of elements in the array.
d. add following array to an array “cars”.
var person=[“Rajan”, “Yagya”, “Munish”];
9. Consider the string “Life is Beautiful”. Write a function ‘mystring’ that performs the following tasks:
a. Displays the length of the string
b. Displays the string after replacing space “ ” in the string with “ * ”
c. Find the position of the first occurrence of “if” and display it.
10. Given an array Classes=[“AI”, “ML”, “DS”, “Security”, “RDBMS”]
What will be the output of the following?
a. document.write(Classes.pop( ))
b. document.write(Classes.push(“NoSQL” ))
c. document.write(Classes.unshift(“Prompt”, “UI”)
d. Write the code to output array Classes in the paragraph with ID= “Class”
Given a string str=’The return statement can be used to return a value at any time’
What will be the output of the following statements?
a. document.write(str.indexOf(‘return’))
b. document.write(str.match(‘to return’))
c. document.write(str.replace(‘value’,’output’))
d. document.write(str.substring(4,10))

