Chapter 5 : MySQL Revision Tour
Sumita Arora Book Exercise Solution of Class 12 Informatics Practices [065]
![]()
Assignment
Consider a table Empl as given below. It will be required for many assignment questions.
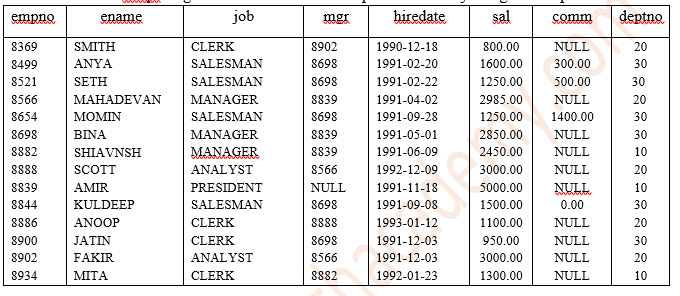
1. How are SQL commands classified?
Answer :- SQL Commands are classified into the following categories –
(a) Data Definition Language (DDL) commands
(b) Data Manipulation Language (DML) commands
(c) Transaction Control Language (TCL) commands
(d) Session Control Commands
(e) System Control Commands
2. Differentiate between DDL and DML commands.
Answer :- DDL stands for Data Definition Language Commands. DDL Commands are used for the definition and alteration of the Database & Tables. The DDL Commands can’t be roll-backed.
DML stands for Data Manipulation Language Command. DML commands are used for the manipulation of records like Insertion of records, updation of records, deletion of records and querying (selecting) records. The DML commands can be roll-backed.
3. (a) What is the use of UPDATE statement in SQL? How is it different from ALTER statement?
Answer :- UPDATE statement in MySQL is use to update the record i.e. values of tuple(s).
UPDATE vs ALTER
- UPDATE is a DML command while ALTER is a DDL command.
- UPDATE is use to change the value of tuple/record while ALTER command is use to change the structure of TABLE like adding , deleting, changing and modifying columns and constraint.
3. (b) Mr. Shankar created a table VEHICLE with 3 rows and 4 columns. He added ‘l more row to it and deleted one column. What is the Cardinality and Degree of the Table VEHICLE?
Answer :- Cardinality of Table VEHICLE (Number of Rows in Table VEHICLE) = 4
Degree of Table VEHICLE (Number of columns in Table VEHICLE) = 3
(c) Consider the following table named “GYM” with details about fitness items being sold in the store. Write command of SQL for (i) to (iv).
Table: GYM
| ICODE | INAME | PRICE | BRANDNAME |
| G101 | Power Fit Exerciser | 20000 | Power Gymea |
| G102 | Aquafit Hand Grip | 1800 | Reliable |
| G103 | Cycle Bike | 14000 | Ecobike |
| G104 | Protoner Extreme Gym | 30000 | Coscore |
| G105 | Message Belt | 5000 | Message Expert |
| G106 | Cross Trainer | 13000 | C,TC Fitness |
(i) To display the names of all the items whose name starts with “A”.
(ii) To display ICODEs and INAMEs of all items, whose Brandname is Reliable or Coscore.
(iii) To change the Brandname to “Fit Trend India” of the item, whose ICODE as “G101”
(iv) Add a new row for new item in GYM with the details:
“G107”, “Vibro exerciser”, 21000, “GTCFitness”
Answer :-
(i) SELECT INAME FROM GYM WHERE INAME LIKE ‘A%’;
(ii) SELECT ICODE, INAME FROM GYM WHERE BRANDNAME IN (‘RELIABLE’ , ‘COSCORE’)
OR
SELECT ICODE, INAME FROM GYM WHERE BRANDNAME = ‘RELIABLE’ OR BRANDNAME = ‘COSCORE’)
(iii) UPDATE GYM SET BRANDNAME = ‘Fit Trend India’ WHERE ICODE = ‘G101’
(iv) INSERT INTO VEHICLE VALUES(“G107”, “Vibro exerciser”, 21000, “GTCFitness”);
4. (a) Mr. James created a table CLIENT with 2 rows and 4 columns. He added 2 more rows to it and deleted one column. What is the Cardinality and Degree of the Table CLIENT?
Answer :- Initially table CLIENT has CARDINALITY – 2 and DEGREE – 4
After adding 2 ROWS and deleted 1 COLUMN, then
Table CLIENT has CARDINALITY – 4, and DEGREE – 3
4. (b) Consider the following table FITNESS with details about fitness products being sold in the store. Write command of SQL for (i) to (iv).
Table: FITNESS
| PCODE | PNAME | PRICE | MANUFACTURER |
| P1 | Treadmill | 21000 | Coscore |
| P2 | Bike | 20000 | Aone |
| P3 | Cross Trainer | 14000 | Reliable |
| P4 | Multi Gym | 34000 | Coscore |
| P5 | Massage Chair | 5500 | Regrosene |
| P6 | Belly Vibrator Belt | 6500 | Ambawya |
(i) To display the names of all the products with price more than 20000.
(ii) To display the names of all products by the manufacturer “Aone”.
(iii) To change the price data of all the products by applying 25% discount reduction.
(iv) To add a new row for product with the details : “P7”, “Vibro Exerciser”, 28000, “Aone”.
Answer :- (i) SELECT PNAME FROM PRODUCT WHERE PRICE > 20000;
(ii) SELECT PNAME FROM PRODUCT WHERE MANUFACTURER = ‘AONE’;
(iii) UPDATE PRODUCT SET PRICE = PRICE – PRICE * 0.25;
(iv) INSERT INTO PRODUCT VALUES(“P7”, “Vibro Exerciser”, 28000, “Aone”);
5. Write SQL commands for the following on the basis of given table CLUB.
Table: CLUB
| COACH_ID | COACHNAME | AGE | SPORTS | DATOFAPP | PAY | SEX |
| 1. | KUKREJA | 35 | KARATE | 27/03/1996 | 1000 | M |
| 2. | RAVINA | 34 | KARATE | 20/01/1998 | 1200 | F |
| 3. | KARAN | 34 | SQUASH | 19/02/1998 | 2000 | M |
| 4. | TARUN | 33 | BASKETBALL | 01/01/1998 | 1500 | M |
| 5. | ZUBIN | 36 | SWIMMING | 12/01/1998 | 750 | M |
| 6. | KETAKI | 36 | SWIMMING | 24/02/1998 | 800 | F |
| 7. | ANKITA | 39 | SQUASH | 20/02/1998 | 2200 | F |
| 8. | ZAREEN | 37 | KARATE | 22/02/1998 | 1100 | F |
| 9. | KUSH | 41 | SWIMMING | 13/01/1998 | 900 | M |
| 10. | SHAILYA | 37 | BASKETBALL | 19/02/1998 | 1700 | M |
(a) To show all information about the swimming coaches in the club.
(b) To list names of all coaches with their date of appointment (DATOFAPP) in descending order.
(c) To display a report, showing coachname, pay, age and bonus (15% of pay) for all the coaches.
Answer :- (a) SELECT * FROM CLUB WHERE SPORTS = ‘SWIMMING’;
(b) SELECT COACHNAME, DATOFAPP FROM CLUB ORDER BY DATOFAPP DESC;
(c) SELECT COACHNAME, PAY, AGE, AGE * 0.15 AS ‘BONUS’ FROM CLUB;
6. Write SQL commands for the following on the basis of given table STUDENT.
Table: STUDENT
| No. | Name | Stipend | Stream | AvgMark | Grade | Class |
| 1 | Karan | 400.00 | Medical | 78.5 | B | 12B |
| 2 | Divakar | 450.00 | Commerce | 89.2 | A | 11C |
| 3 | Divya | 300.00 | Commerce | 68.6 | C | 12C |
| 4 | Arun | 350.00 | Humanities | 73.1 | B | 12C |
| 5 | Sabina | 500.00 | Nonmedical | 90.6 | A | 11A |
| 6 | John | 400.00 | Medical | 75.4 | B | 12B |
| 7 | Robert | 250.00 | Humanities | 64.4 | C | 11A |
| 8 | Rubina | 450.00 | Nonmedical | 88.5 | A | 12A |
| 9 | Vikas | 500.00 | Nonmedical | 92.0 | A | 12A |
| 10 | Mohan | 300.00 | Commerce | 67.5 | C | 12C |
(a) Select all the Nonmedical stream students from STUDENT.
(b) List the names of those students who are in class 12 sorted by Stipend.
(c) List all students sorted by AvgMark in descending order.
Answer :- (a) SELECT * FROM STUDENT WHERE STREAM = ‘NONMEDICAL’ ;
(b) SELECT * FROM STUDENT WHERE CLASS LIKE ‘12%’ ORDER BY STIPEND;
(c) SELECT * FROM STUDENT ORDER BY AVGMARK DESC ;
7. What is foreign key? How do you define a foreign key in your table?
Answer :- Foreign Key is a non-key attribute, which value is derived from the primary key of other table.
Foreign Key constraint is define with the help of REFERENCES clause in SELECT statement. For example:
Student(admno, name, class_sec) #admno is primary key
Fee(fid, amount, fdate, admno) #fid is primary key, while admno is a foreign key.
CREATE TABLE Student ( admno int(4) PRIMARY KEY, name char(20), class_sec char(10) );
CREATE TABLE Fee ( fid int(3) PRIMARY KEY, amount decimal(10,2), fdate date, admno int(4) REFERENCES Student(admno) );
OR
CREATE TABLE Fee (fid int(3) PRIMARY KEY, amount decimal(10,2), fdate date, admno int(4), FOREIGN KEY (admno) REFERENCES Student(admno) );
- How is FOREIGN KEY commands different from PRIMARY KEY command?
Answer: Foreign Key allows duplicate and NULL value while Primary Key does not allow duplicate & NULL value.
9. How is FOREIGN KEY commands related to the PRIMARY KEY?
Answer :- As you know, Foreign Key is a non-key attribute of a table, which value is derived from primary key of the other table.
The value of Foreign key is always depending upon the Primary Key; it means it can contain either NULL or the value existing in Primary key column.
10. What are table constraints? What are column constraints? How are these two different?
Answer :- Table Constraint:
11. Insert all those records of table Accounts into table Pending where amt_outstanding is more than 10000.
Answer :- INSERT INTO PENDING SELECT * FROM ACCOUNTS WHERE amt_outstanding > 10000;
12. Increase salary of employee records by 10% (table employee).
Answer :- UPDATE emp SET sal = sal + sal * 0.10;
13. Add a constraint (NN-Grade) in table Empl (given before assignment) that declares column Grade not null.
Answer :-
14. Drop the table Empl.
Answer :- DROP TABLE Empl;
15. Differentiate between
(i) DROP TABLE, DROP DATABASE
(ii) DROP TABLE, DROP clause of ALTER TABLE.
Answer :- (i) DROP TABLE, DROP DATABASE
DROP TABLE deletes a TABLE from a database, while DROP DATABASE will delete database, i.e. delete all tables including with DATABASE.
Answer :- (ii) DROP TABLE, DROP clause of ALTER TABLE
DROP TABLE command is delete a table with all columns and rows, while DROP clause of ALTER TABLE will delete a column from a table, It will not delete entire table.
16. Mr. Mittal is using a table with following columns:
Name, Class, Stream_ld, Stream_name
He needs to display names of students who have not been assigned any stream or have been assigned stream_name that ends with “computers”.
He wrote the following command, which did not give the desired result.
SELECT Name, Class FROM Students
WHERE Stream_name = NULL OR Stream name = ‘%computers” ;
Help Mr. Mittal to run the query by removing the error and write correct query.
Answer :- SELECT Name, Class FROM Students
WHERE Stream_name IS NULL OR Stream_name LIKE ‘%computers” ;
17. The Doc_name Column of a table Hospital is given below:
| Doc_name |
| Avinash |
| Hariharan |
| Vinayak |
| Deepak |
| Sanjeev |
Based on the information, find the output of the following queries:
(i) SELECT doc_name FROM HOSPITAL WHERE Doc_name like “%v”;
Answer :- Output: –
| Doc_name |
| Sanjeev |
(ii) SELECT doc_name FROM HOSPITAL WHERE doc_name like “%e%”;
Answer :- Output: –
| Doc_name |
| Deepak |
| Sanjeev |
18. Sarthak, a student of class XII, created a table “Class”. Grade is one of the columns of this table. To find the details of students whose Grades have not been entered, he wrote the following MySql query, which did not give the desired result:
SELECT * FROM class WHERE Grade = “Null”;
Help Sarthak to run the query by removing the errors from the query and write the correct query.
Answer :- SELECT * FROM class WHERE Grade IS NULL;
19. What is the purpose of ALTER TABLE command? Can you add new columns with constraints such as NOT NULL? Give example to justify your answer.
Answer :-
20. What is the purpose of DROP TABLE command in MySql? How is it different from DELETE command?
Answer :- The DROP TABLE Command in MySQL is use to delete the table permanently with their records. It is DDL Command and you can’t be roll backed i.e. once deleted cannot be recovered back.
It is different from DELETE Command.
- DROP TABLE is a DDL Command while DELETE is a DML Command.
- DROP TABLE delete complete table i.e table and records all together, while DELETE command deletes only record not a Table.
Class 12 Informatics Practices (065) – Sumita Arora Solution
- Class 12 Informatics Practices 065 Ch 4 Importing Exporting Data Between CSV Files MySQL and Pandas Sumita Arora Book Exercise Solution
- Class 12 Informatics Practices 065 Ch 3 Plotting with PyPlot Sumita Arora Book Exercise Solution
- Class 12 Informatics Practices Chapter 6 MySQL Functions Assignments Sumita Arora Exercise Solution
- Class 12 Informatics Practices Chapter 6 MySQL Functions Check Point Sumita Arora Exercise Solution
- Class 12 IP 065 Chapter 9 Introduction to Computer Networks Assignments Sumita Arora Solution






